Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
-
Whatsapp


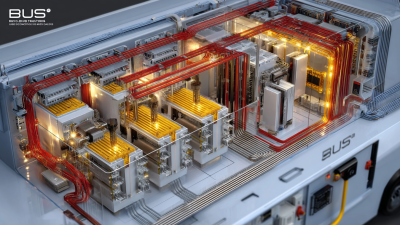
 In modern electrical distribution systems, the efficiency and
reliability of power delivery are paramount, and one
critical component that contributes significantly to these factors is the bus duct.
According to industry reports, the global bus duct market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6%
from 2021 to 2026, driven by the increasing demand for
energy-efficient infrastructure. Bus duct systems, which are used to conduct electricity from one
point to another, play a vital role in enhancing the safety and performance of electrical networks. With their ability to handle high currents
and provide compact, insulated pathways for power distribution,
bus ducts are becoming increasingly essential in commercial and industrial applications. Understanding the role of bus duct in electrical systems
not only helps in optimizing energy use but also ensures compliance with safety standards and operational efficiency.
In modern electrical distribution systems, the efficiency and
reliability of power delivery are paramount, and one
critical component that contributes significantly to these factors is the bus duct.
According to industry reports, the global bus duct market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6%
from 2021 to 2026, driven by the increasing demand for
energy-efficient infrastructure. Bus duct systems, which are used to conduct electricity from one
point to another, play a vital role in enhancing the safety and performance of electrical networks. With their ability to handle high currents
and provide compact, insulated pathways for power distribution,
bus ducts are becoming increasingly essential in commercial and industrial applications. Understanding the role of bus duct in electrical systems
not only helps in optimizing energy use but also ensures compliance with safety standards and operational efficiency.
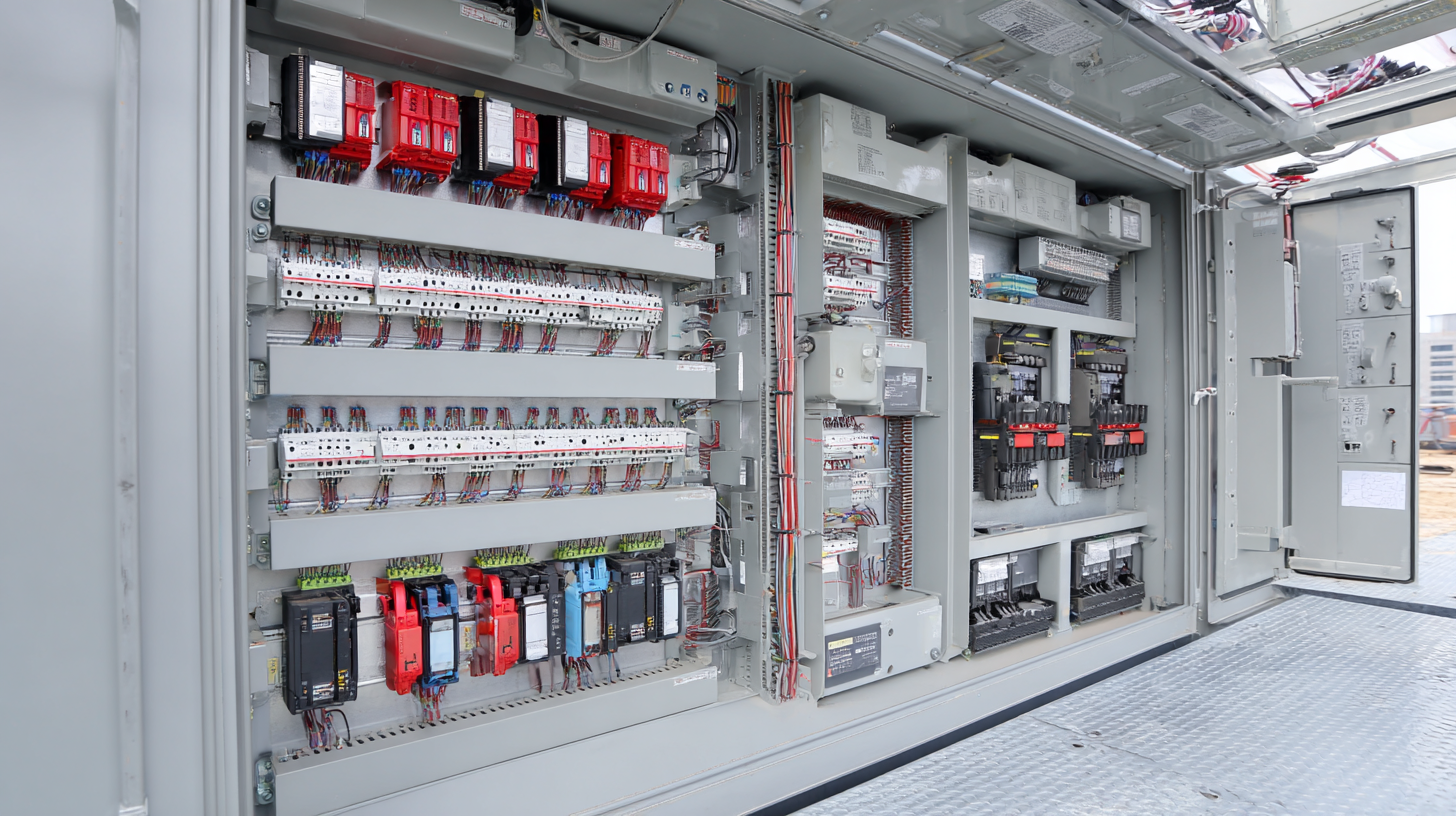
 Bus ducts are essential components within electrical distribution systems, designed to efficiently conduct electricity from one point to another. Their primary function is to house and protect electrical busbars, which are conductive strips or bars that distribute electricity to various circuits. By combining the functionality of conductors and enclosures, bus ducts minimize the risk of electrical overload and disruptions while maximizing space utilization. This allows for a more organized layout in electrical rooms or facilities, ensuring that the entire system operates safely and effectively.
Bus ducts are essential components within electrical distribution systems, designed to efficiently conduct electricity from one point to another. Their primary function is to house and protect electrical busbars, which are conductive strips or bars that distribute electricity to various circuits. By combining the functionality of conductors and enclosures, bus ducts minimize the risk of electrical overload and disruptions while maximizing space utilization. This allows for a more organized layout in electrical rooms or facilities, ensuring that the entire system operates safely and effectively.
In addition to enhancing safety and organization, bus ducts provide significant advantages in terms of scalability and flexibility. As electrical demands change, bus ducts can be easily expanded or modified to accommodate new loads or equipment without the need for extensive wiring alterations. This adaptability makes them particularly beneficial in industrial settings where power requirements may fluctuate over time. Moreover, the design of bus ducts allows for efficient heat dissipation, which is crucial for maintaining optimal operating conditions and prolonging the life of electrical components.
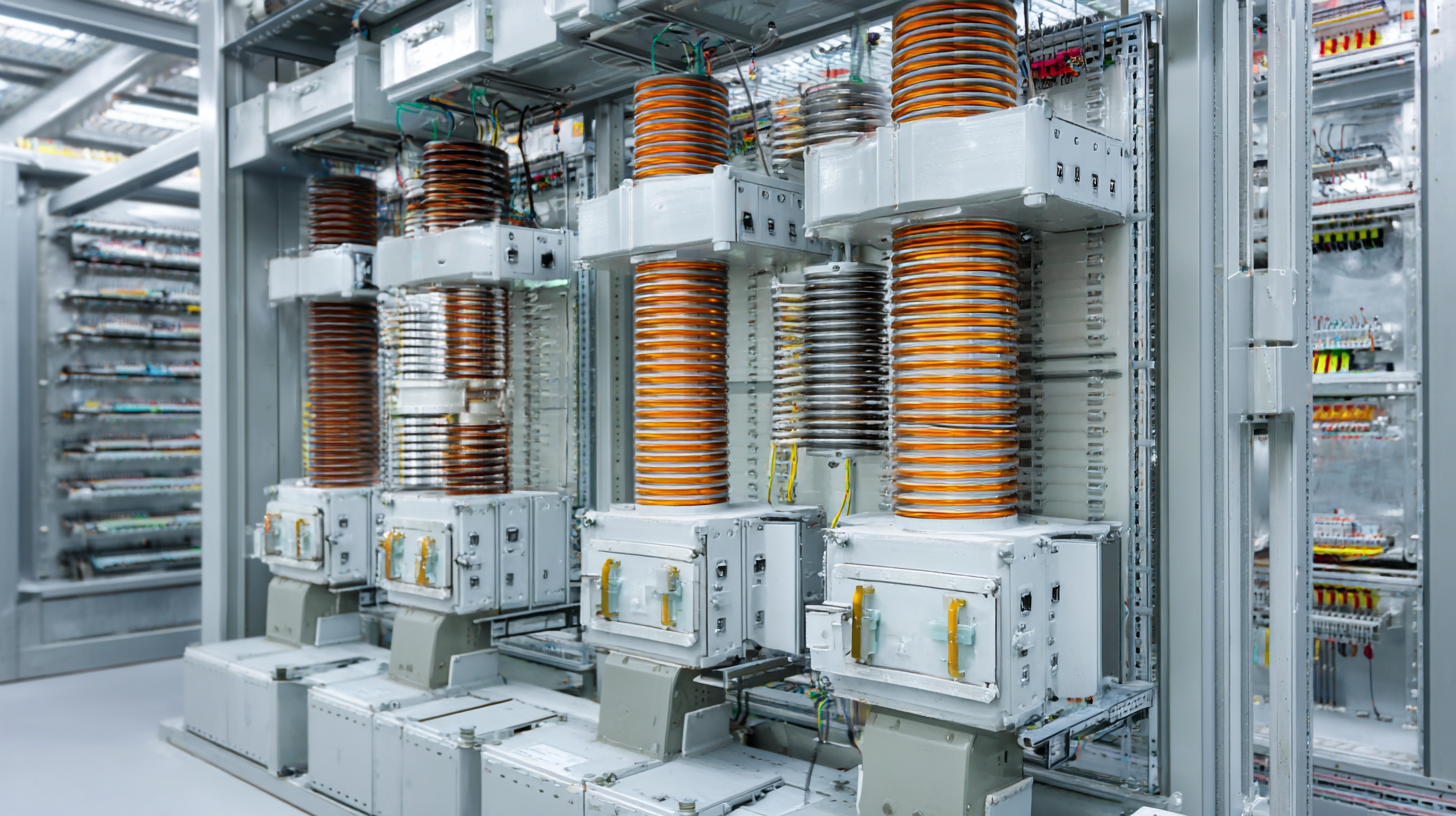
Bus ducts play a crucial role in electrical distribution systems, especially within industrial applications where efficiency and reliability are paramount.
One of the key advantages of using bus duct systems is their superior space-saving design compared to traditional cable systems. According to a report by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), bus ducts can reduce the needed installation space by up to 40%, which not only optimizes the layout of industrial facilities but also lowers construction and labor costs.
Another significant benefit of bus ducts is their enhanced thermal management capabilities. A study published in the Journal of Electrical Engineering indicates that bus ducts have a higher current-carrying capacity, allowing them to handle power distribution more effectively than conventional wiring methods. This efficiency can lead to a reduction in operating temperatures, which subsequently extends the lifespan of electrical components. Furthermore, with an improved immunity to environmental factors like moisture and dust, bus ducts can provide added reliability and safety in demanding industrial settings.
When it comes to electrical distribution systems, the choice between bus ducts and traditional wiring solutions is essential for optimizing performance and efficiency. Bus ducts are known for their ability to handle high load capacities while occupying less physical space compared to traditional wiring methods. This is largely due to their compact design, which allows more straightforward installation and reduced labor costs. Moreover, they provide excellent thermal management, minimizing the risk of overheating, which is a common concern with conventional wiring systems.
In contrast, traditional wiring solutions typically require more extensive physical space, especially when dealing with high current requirements. The installation process can be more time-consuming, involving multiple connections and junction boxes that may lead to potential failure points. Additionally, traditional wiring is prone to wear and damage over time, which can result in costly maintenance and downtime. Therefore, bus ducts offer a modern alternative that not only simplifies the installation process but also enhances the reliability of electrical distribution systems, making them a preferred choice for many commercial and industrial applications.
| Comparison Dimension | Bus Duct | Traditional Wiring |
|---|---|---|
| Installation Complexity | Lower complexity, faster installation | Higher complexity, more labor-intensive |
| Space Efficiency | Compact design, saves space | Requires more space for installation |
| Current Carrying Capacity | Higher capacity, suitable for large loads | Limited capacity, may need multiple lines |
| Maintenance | Easier maintenance with accessible components | Difficult to access, more challenging to maintain |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher initial cost, lower long-term costs | Lower initial cost, higher long-term costs |
| Heat Dissipation | Better heat dissipation, cooler operation | Poor heat dissipation, risk of overheating |
When it comes to the installation and maintenance of bus duct systems, adhering to best practices is crucial to ensure efficiency and longevity. Bus ducts, typically used for conducting electricity along a defined path, require precise installation to prevent issues such as overheating or electrical failures. According to a report by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), improper installation can lead to a 25% increase in maintenance costs over time. Therefore, following manufacturer guidelines and employing skilled technicians during installation is paramount.
Regular maintenance is equally important for bus duct systems, as periodic inspections can detect potential issues before they escalate. Industry standards recommend a quarterly inspection schedule, which includes checking for signs of wear, loose connections, and ensuring that all insulating materials are intact. The Maintenance, Repair, and Operations (MRO) industry highlights that effective maintenance can reduce downtime by up to 30% and extend the lifespan of bus duct components significantly. By prioritizing these best practices, organizations can enhance the reliability and safety of their electrical distribution systems, ultimately contributing to better operational efficiency.
In modern electrical distribution systems, bus ducts play a critical role in enhancing energy efficiency in facilities. With advancements in technology, innovative bus duct features have emerged to optimize power distribution while minimizing energy losses. For example, studies show that using aluminum bus ducts instead of traditional copper options can reduce weight and improve thermal efficiency, resulting in potential energy savings of up to 10% (International Energy Agency, 2022). This reduction not only helps in lowering operational costs but also reduces the overall carbon footprint of electrical systems.
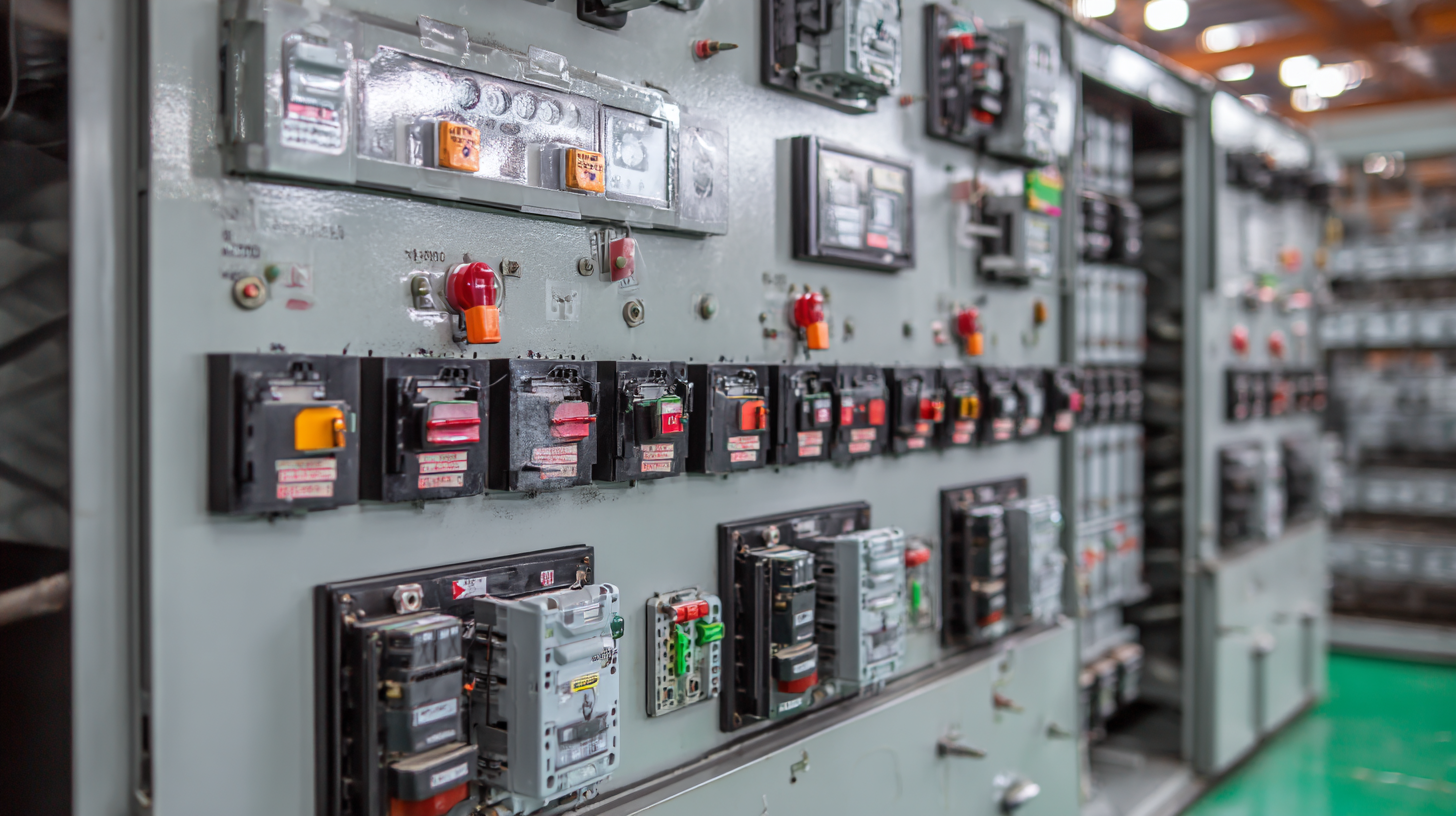
Moreover, the integration of advanced insulation materials in bus ducts significantly enhances their performance. These materials can withstand higher temperatures and improve thermal conductivity, leading to more stable and reliable energy distribution. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, facilities incorporating modern bus duct systems equipped with improved insulation report a decrease in energy consumption by approximately 15% (U.S. DOE, 2023). Such innovative features not only support energy efficiency but also promote sustainability within the built environment, aligning with global initiatives to reduce energy use and tackle climate change.